When building or renovating a home or business, choosing the right insulation is crucial. If you need effective thermal protection, fiberglass is one of the most popular materials available today. This type of insulation has been used in homes since the 1930s and was first created by the Owens Corning Company. Over its long history, it has remained a staple in modern construction due to its ability to make spaces energy-efficient. Made from fine glass fibers, it effectively reduces heat loss, keeping your space comfortable year-round. Whether you’re working on an attic, wall, or another part of your property, it’s wise to consider insulating with fiberglass. It’s a go-to choice for those looking to improve efficiency while maintaining affordability.
What is Fiberglass Insulation?
Fiberglass insulation is a material made from extremely fine glass fibers, designed to reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency. It is commonly found in homes and commercial buildings due to its affordability and effectiveness. This insulation is used in different types, including batts, rolls, loose-fill, rigid boards, and duct insulation. These variations allow it to fit various construction needs, whether for unfinished walls, floors, ceilings, or HVAC systems.
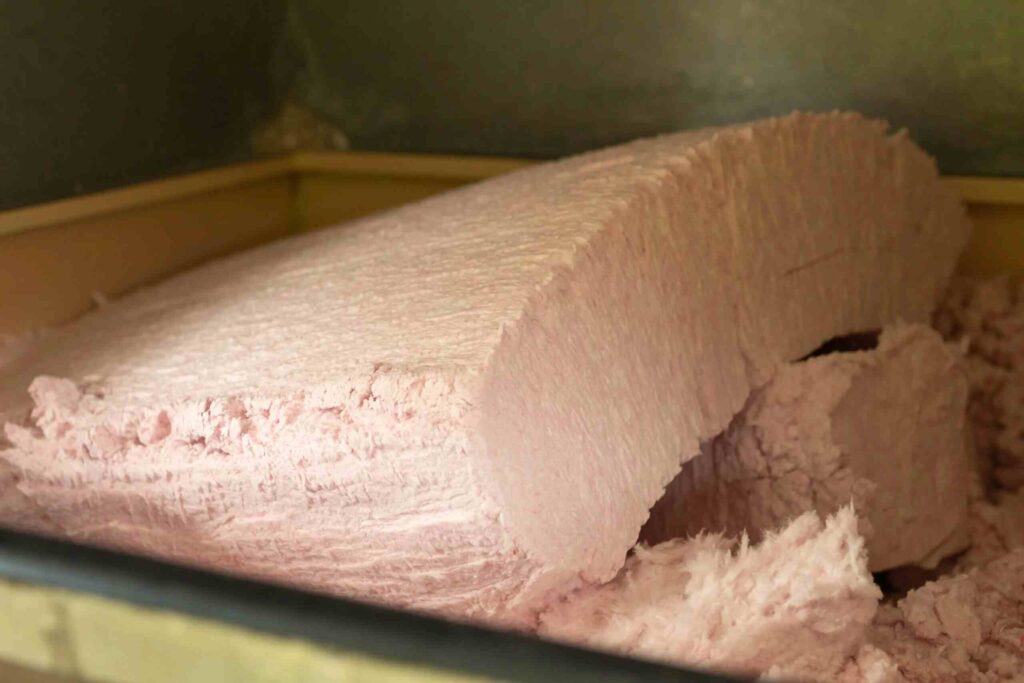

Manufacturers produce medium and high-density batt products, which offer a slightly higher R-Value compared to standard insulation, as noted by the U.S. Department of Energy. Fiberglass is typically placed between studs, joists, and beams, helping to slow the spread of heat and cold. It is a preferred choice for residential and commercial projects, providing a good option for homeowners looking to save dollars on energy costs. Whether handled as a do-it-yourself installation or professionally fitted, fiberglass insulation remains a reliable and efficient solution.
What Is Fiberglass Insulation Made Of?
Fiberglass insulation is made from molten glass that is spun or blown into fine fibers. These fibers are then bonded together to form insulation materials that help resist heat flow and improve energy efficiency. Manufacturers use between 40% to 60% recycled content, making fiberglass an eco-friendly option.
To create fiberglass, various raw materials are used, including silica, sand, limestone, soda ash, borax, calcinated alumina, feldspar, kaolin clay, magnesite, and nepheline syenite. This mixture is melted and processed into continuous or discontinuous fibers, which are then formed into different applications like batts, loose-fill, blankets, rigid boards, and Blow-In-Blanket System® (BIBS). The insulation-blowing machine is commonly used for open-blow applications in attic spaces or closed-cavity walls and floors. Fiberglass can also be found in drapes, shower curtains, window frames, roof shingles, and other household items, proving its versatile coverage and effective method in both construction and insulation industries.
How Fiberglass Insulation Works
Fiberglass insulation works by using fine glass fibers to trap pockets of air, which helps slow the movement of heat. When installed in a building, it creates a barrier that helps keep conditioned air inside, reducing heating and cooling costs. In the winter, it prevents heat from escaping, while in the summer, it stops hot air from intruding into the home. The physics behind this process is simple—air is a poor conductor, so these small air pockets act as a buffer against temperature fluctuations.
The effectiveness of fiberglass insulation is quantified using R-value, which measures thermal resistance. A higher R-value means greater ability to resist heat flow. Typically, fiberglass insulation has an R-value ranging between 2.1 and 2.7 per inch, making it an efficient and cost-effective material for insulation. The insulation process works by forcing heat to pass through multiple layers, slowing down its movement and impeding external temperature changes. Whether for home or commercial use, fiberglass insulation remains a valuable option for maintaining indoor comfort and energy efficiency.
Different Types of Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation is available in different forms, each tailored for specific applications in homes and buildings. The most common types are batts, rolls, and loose-fill insulation, all designed for easy installation in walls, attics, and floors. These methods help regulate indoor temperatures and improve energy efficiency. Choosing the right type depends on the area being insulated and the structure of the space.
Batts and Rolls – A Versatile Insulation Option
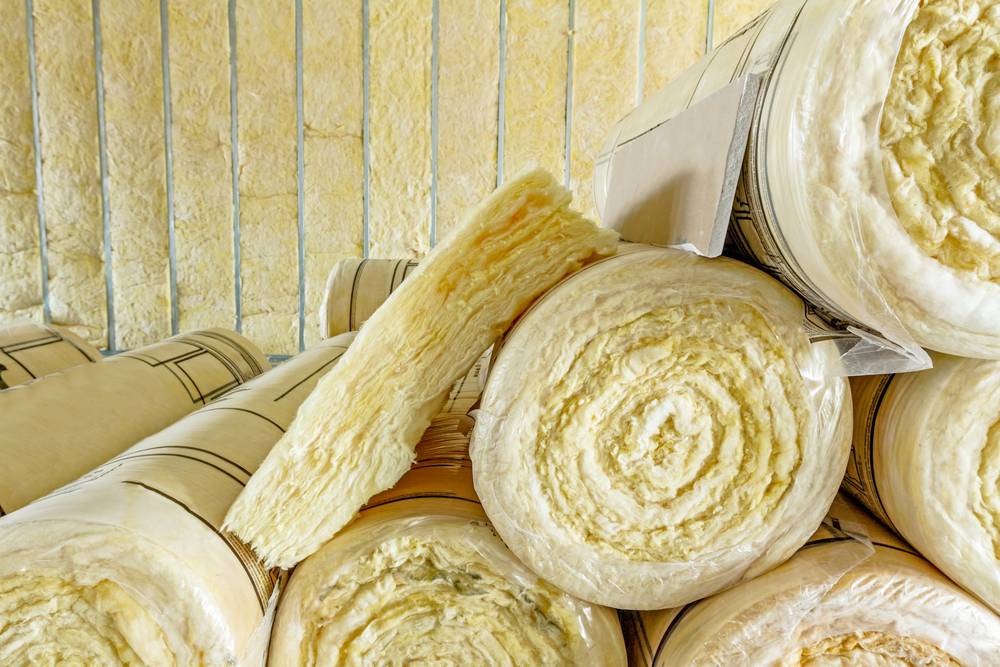
Among the most widely used options, batts and rolls offer a recognized and flexible form of insulation. These pre-cut sheets are designed to snugly fit between wall studs, ceiling joists, and floor spaces, making them a favorite choice for DIY enthusiasts and professional installers. The batt insulation comes in rectangular or square pieces, while rolls are continuous sheets that can be wound for transport. The thickness of batts and rolls varies, with thicker insulation providing better ceiling coverage. Installation is straightforward—simply measure the space, cut the insulation to fit, and place it into the cavity. This makes batts and rolls an excellent choice for insulating walls, attics, and floors, offering ease of handling and versatility for any insulation project.

Loose-Fill Insulation – A Smart Choice for Hard-to-Reach Areas
Loose-fill fiberglass insulation is exactly what its name suggests—it consists of loose fibers and granules that can be blown or poured into tight spaces to create a seamless layer of thermal protection. This type of insulation is particularly handy for hard-to-reach areas like irregularly shaped attics, existing walls, and crawl spaces where traditional insulation methods may not work. The installation process requires specialized equipment to distribute the insulation evenly, ensuring it conforms to the shape of the space while effectively filling every nook and cranny.
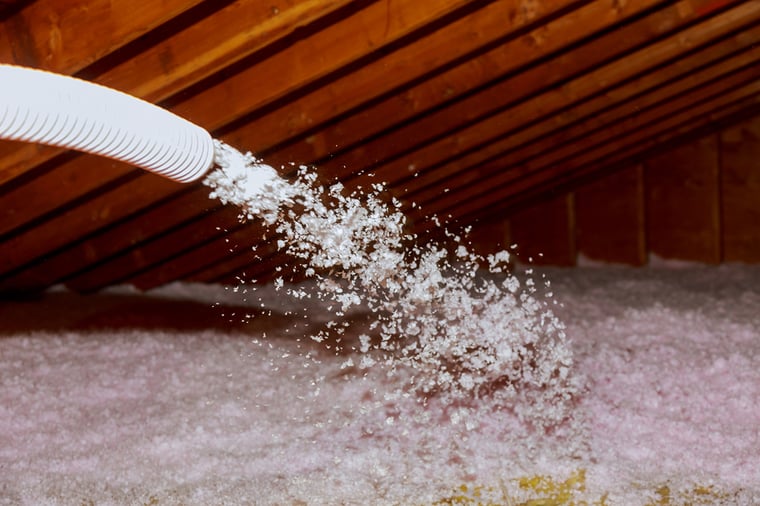

One notable advantage of loose-fill insulation is its ability to provide a higher R-value, leading to greater energy savings. It is a versatile solution that helps boost thermal performance, making it a great choice for homeowners looking for an efficient and customizable option. While batts and rolls are more standard, loose-fill excels in unconventional applications, especially where achieving complete coverage is challenging. Whether you’re adding insulation to an existing home or working on a new build, loose-fill insulation depends on specific needs and layout, offering an effective and user-friendly installation method.
Also Read: Is Blown-In Insulation Better Than Batts? Pros & Cons
Pros and Cons of Fiberglass Insulation
When considering the right insulation material for your home, it’s important to weigh both the benefits and problems before buying. Fiberglass insulation is a widely used option because of its affordability and effectiveness, but like any material, it has advantages and drawbacks.
Fiberglass Insulation Pros
- Relatively inexpensive compared to other insulation options.
- Suited for standard stud and joist spacing, making installation easier.
- Works well in areas free from obstructions, allowing for a smooth fit.
- A great option for DIY projects, reducing installation costs.
Fiberglass Insulation Cons
- Small particles can come into contact with skin, lodge in pores, and cause itchiness, rashes, and irritation.
- Allows airflow, which can be a major source of high energy bills and an uncomfortable room temperature.
- If inhaled, it may cause coughing, nosebleeds, and respiratory ailments.
- When disturbed, releases particulates into the air, affecting those installing or removing it.
- Those handling fiberglass should wear gloves, long-sleeved shirts, pants, and goggles to prevent irritation.
- Can trap allergens, dust, and moisture, which may lead to mold growth over time.
Proper Installation of Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation is commonly found in attics, crawl spaces, open walls, and floors, providing an effective way to control temperature. It is available in different forms, including blanket insulation called batts and loose-fill insulation, which is a great insulation option for crawl space areas, as it can be blown into cavities. Batts usually come in pre-cut standard lengths and widths, making them easy to work with. They are stapled into place and often manufactured with paper or foil backing, which should always face the direction of warmth to improve effectiveness.
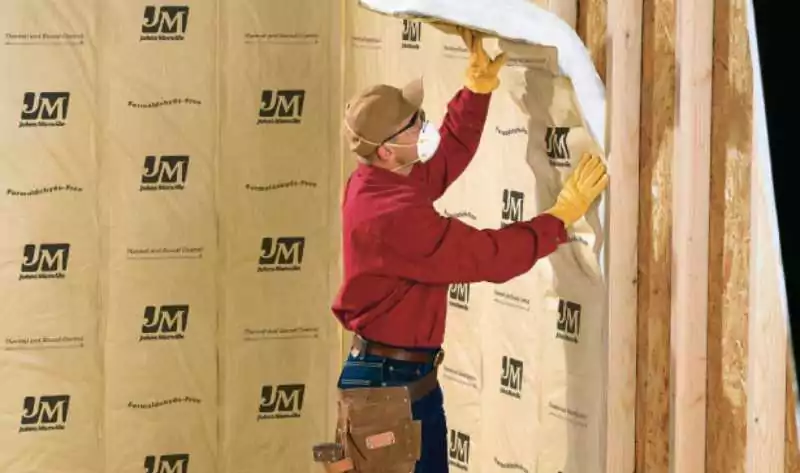

To ensure fiberglass is installed correctly, it is essential to create a barrier that slows the passage of moisture and prevents fibrous particles from entering the home. Improper installation can increase the likelihood of insulation not performing efficiently. According to InterNACHI, a common mistake is not placing the backing towards the warm side of the structure, reducing its insulating ability. Whether using batts or loose-fill insulation, following proper techniques will help maximize energy efficiency and warmth retention.
Important Tips for Installing Fiberglass Insulation
When considering installing fiberglass insulation in your home or business, it’s essential to keep a few key considerations in mind. Whether you plan to do it yourself or hire a professional, proper installation ensures maximum energy efficiency. Fiberglass should be installed correctly to prevent gaps, compression, or air leaks that reduce its effectiveness. To get the best results, follow important tips that will help you achieve a well-insulated space while minimizing waste and potential health risks.
Tips for DIY Installation
- Measure Twice, Cut Once – Taking accurate measurements is crucial. Double-check before cutting to minimize waste.
- Wear Safety Gear – Always wear appropriate protection, including gloves, a dust mask, long sleeves, and safety glasses, to protect yourself from fiberglass particles.
- Gather Necessary Tools – Have a utility knife, straightedge, and sturdy step ladder ready before starting installation to avoid delays.
- Seal Gaps and Cracks – Use caulk or foam sealant to seal cracks in the building envelope, which helps maximize effectiveness and prevents air leaks.
- Ensure Proper Placement – Batts and rolls should fit snugly without compressing the material, as overstuffing or leaving gaps can reduce insulation performance.
- Hire Professionals If Needed – If you lack protective gear or the right skills to install insulation, it’s best to hire professionals to handle the task safely and efficiently.
Safety Measures for Installing Fiberglass Insulation
When installing fiberglass insulation, taking the right safety precautions is important to avoid health risks. The installation area should have proper ventilation to disperse airborne particles, so always open windows and doors when working in enclosed spaces. Wearing protective gear is necessary to minimize contact with fiberglass particles, which can cause skin irritation and respiratory issues. Following these precautions ensures a safe working environment while maintaining good indoor air circulation.
Safety Precautions to Follow
- Wear Protective Gear – Always wear a respirator, gloves, long-sleeved clothing, and eye protection to prevent exposure.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation – Keep windows and doors open to allow fresh air to remove airborne fiberglass particles.
- Avoid Inhaling Dust – Use a rated respirator to prevent inhaling fine particles during installation.
- Maintain Cleanliness – Wash hands thoroughly after completing work, and clean any exposed clothing separately to prevent spreading fibers.
- Cover Exposed Skin – Wear appropriate clothing to reduce contact, as fiberglass can cause irritation on uncovered areas.
Choosing the Right Professionals for Insulation Installation
When hiring insulation professionals, it is important to research and select reputable contractors to ensure a successful installation. Always seek recommendations and check references before making a decision. A proven track record is key, so request multiple quotes instead of settling for the first estimate you receive. Compare different offers carefully to ensure a fair price, and don’t forget to ask about warranties and what’s included in the package. Clear communication about requirements and expectations helps avoid misunderstandings, so it’s best to agree on a timeframe to minimize inconvenience in your home.
Key Factors to Consider When Hiring Professionals
- Verify Licensing and Insurance – Ensure the contractor is licensed and insured to protect your property and give you peace of mind in case of unforeseen issues.
- Check for Safety Measures – Ask about the safety protocols they follow during installation to protect their crew and your home.
- Compare Multiple Quotes – Reviewing different estimates helps ensure a fair price and gives insight into what’s included in the offer.
- Specify Your Needs – Be clear about requirements and expectations to prevent errors and delays.
- Inquire About Warranties – A professional contractor should provide warranties to cover any potential issues after installation.
How Fiberglass Insulation Affects Energy Costs
Fiberglass insulation is one of the most traditional forms of insulation, designed to be resistant to heat transferred through conduction. However, this does not always mean it is the most efficient option. Some materials tend to poorly protect against air flow, leading to energy loss and contributing to discomfort in the home. If not installed correctly, gaps in insulation may allow heat to escape in the winter and enter during the summer, forcing heating and cooling systems to work harder and increasing energy costs.
Safety and Potential Risks of Fiberglass Insulation
Safety of Fiberglass Insulation in Homes
Fiberglass insulation is an excellent choice for homes because it is fire-resistant without additives, making it a safe option from a fire safety perspective. However, it is important to not handle it with bare hands, as the tiny glass particles can irritate the skin and sometimes cause a rash. Inhalation of these fibers can also result in coughing and other respiratory ailments. While installation should be left to an experienced professional, once in place, fiberglass poses no health risks or safety hazards for homeowners.
Potential Risks of Fiberglass Insulation
When fiberglass insulation is disturbed, it releases particulates into the air, which can be inhaled by workers installing or removing it. This is a concern for property inspectors and anyone crawling through attics or crawlspaces where insulation is present. To stay safe, always wear gloves, a long-sleeved shirt, pants, goggles, and a dust mask. For the greatest protection in certain circumstances, using a respirator with a particulate filter is recommended to prevent inhalation of potentially irritating fibers.
Before removing fiberglass insulation, it’s a good idea to dampen the area to keep particles from entering the airspace. Afterwards, wash your hands with water—preferably cold, since warm water can expand pores, making it easier for fibers to trap and travel deeper into the skin. Taking these precautions can help reduce exposure and discomfort when working with fiberglass insulation.
Final Thoughts
Fiberglass insulation is a time-tested solution that offers both energy conservation and home comfort. Its dynamic thermal performance helps slash energy bills over time, making it an unrivaled material in insulation. With a low price and hassle-free installation requirements, it continues to be a unique choice for homeowners looking for the most bang for their buck. Its ability to provide long-term efficiency ensures that homes remain insulated while keeping costs under control. Whether upgrading an existing system or working on new construction, fiberglass insulation gives a reliable and effective way to maintain indoor comfort while contributing to a more energy-efficient future.
FAQ
What Are the Ingredients in Fiberglass Insulation?
Fiberglass insulation is made from glass fibers and includes several raw materials such as silica, sand, limestone, soda ash, and borax. Other primary ingredients in its production include calcinated alumina, feldspar, kaolin clay, magnesite, and nepheline syenite. These basic materials are melted and processed to form insulation, making it lightweight and thermally efficient.
What Is the Biggest Problem With Fiberglass Insulation?
One major issue with fiberglass insulation is air leakage because it is less dense than other types. It does not create an airtight seal, which means air can travel freely through the insulation. This common problem is a source of energy loss in a house, making heating and cooling systems work harder.
Is Fiberglass as Bad as Asbestos?
Fiberglass insulation is generally considered less dangerous than asbestos. While it can cause skin, eye, and respiratory irritation, it is not known to cause cancer like asbestos. Asbestos is a proven carcinogen linked to lung cancer and mesothelioma, making it far more hazardous.
Is Fiberglass Insulation Hazardous?
Fiberglass insulation can be hazardous if inhaled, as it poses significant respiratory risks. The minuscule material can enter breathing passageways, where it goes through the body and creates tiny cuts around organs and tissues. Proper handling and protective gear can help reduce exposure.

1 thought on “What Is Fiberglass Insulation Made Of? Don’t Ignore This!”